Cradle to oprogramowanie do symulacji CFD (Computational fluid dynamics), które służy do symulacji numerycznych przepływu cieczy i gazów. Umożliwia ono analizowanie rozmaitych scenariuszy i warunków przepływu, co pozwala na dokładniejsze zrozumienie zachowania cieczy i gazów w różnych, specyficznych warunkach. Program Cradle to zintegrowane narzędzie symulacyjne, które charakteryzuje się wysoką niezawodnością i szybkością realizacji obliczeń, co czyni go doskonałym narzędziem wspomagania prac projektowych i rozwojowych produktu lub procesu.
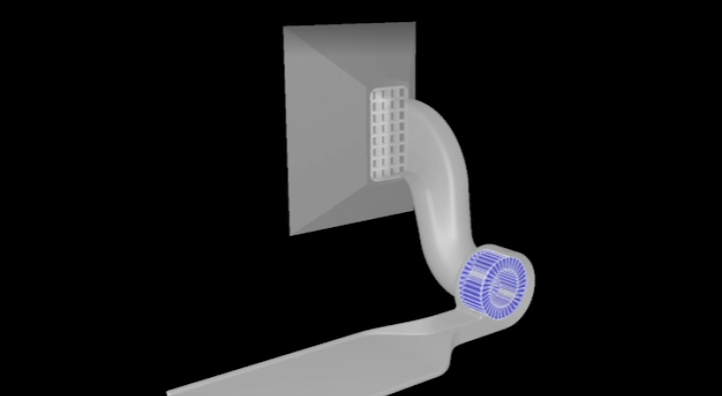
Kliknij aby obejrzeć nagranie symulacji CFD w scFLOW.
Wszechstronny program do CFD
Program do CFD – Cradle, może być również wykorzystywany do przewidywania parametrów produktów, w przypadku kiedy trudno jest wykonać pomiary eksperymentalne. Ponadto analizy numeryczne można wykorzystać do wizualizacji niewidocznego lub trudnego do eksperymentalnej wizualizacji przepływu i wymiany ciepła. Skutkuje to lepszym zrozumieniem analizowanych zagadnień inżynierskich, a jednocześnie zapewnia możliwość przekazania tej wiedzy osobom niebędącymi ekspertami.
Dzięki temu, że obliczenia numeryczne umożliwiają wyznaczanie parametrów technicznych bez konieczności tworzenia fizycznego prototypu, narzędzia symulacyjne można wykorzystywać już w wczesnym etapie planowania rozwoju produktu, aby przeanalizować wstępne koncepcje projektowe.
Analizy aerodynamiczne
Aerodynamika jest ważną dziedziną projektowania i inżynierii, ponieważ ma bezpośrednie przełożenie na wydajność i bezpieczeństwo statków powietrznych, pojazdów lub budynków. Jest również programem do analiz aerodynamicznych, który pozwala na symulację przepływu powietrza wokół różnych obiektów, takich jak samoloty, pojazdy, budynki czy turbiny wiatrowe. Umożliwia określenie różnych wielkości aerodynamicznych, takich jak siły i momenty aerodynamiczne, pola ciśnienia, prędkości, temperatury, początek oderwania, wizualizacje olejowe, itd.
scSTREAM i HeatDesigner z siatką kartezjańską (strukturalną)
Narzędzia scSTREAM i HeatDesigner służą przemysłowi elektronicznemu i architektonicznemu od ponad trzydziestu lat. Stale rozwijane oprogramowanie do CFD, charakteryzuje się przyjaznym interfejsem użytkownika oraz dużą szybkością obliczeń i przetwarzania danych. HeatDesigner jest oparty na scSTREAM i został specjalnie opracowany do projektowania cieplnego produktów elektronicznych. HeatDesigner zapewnia funkcje fizyczne wymagane tylko w projektowaniu cieplnym, dzięki prostemu interfejsowi i dużej wydajności obliczeniowej.
scSTREAM i HeatDesigner – przykładowe zastosowania:
- Projektowanie przepływu powietrza i wymiany ciepła w pomieszczeniach zamkniętych
- Aerodynamika małych prędkości, zarówno przepływy wewnętrzne, jak i zewnętrzne
- Analizy klimatyczne i urbanistyczne
- Projektowanie wymiany ciepła w elektronice i instrumentach precyzyjnych
- Ocena odporności elektroniki i przyrządów precyzyjnych na kurz i wilgoć
- Analizy przepływów wielofazowych, takich jak mieszanie, rozpylanie, krzepnięcie, topnienie, wrzenie i kondensacja
- Analizy z udziałem obiektów ruchomych, takich jak samochody, pociągi, urządzenia sterowane, urządzenia hydrauliczne i pneumatyczne oraz roboty
scFLOW i SC/Tetra z siatką niestrukturalną
SC/Tetra charakteryzuje się wydajną i szybką techniką generowania siatki, dużą wydajnością obliczeniową i przyjaznym dla użytkownika interfejsem. Zaawansowaną wersją jest program scFLOW. Jest on wyposażony w solver, który osiąga trzykrotnie większą szybkość obliczeń niż poprzednio, oraz nowy preprocesor, który pomaga początkującym użytkownikom budować skomplikowane modele z siatką wysokiej jakości. scFLOW jest oprogramowaniem nowej generacji, które stale się rozwija.
scFLOW i SC/Tetra – przykładowe zastosowania:
- Symulacje aerodynamiczne statków powietrznych i pojazdów.
- Obliczenia maszyn wirnikowych, takich jak wentylatory i pompy.
- Obliczenia z uwzględnieniem kawitacji i erozji.
- Projektowanie urządzeń AGD, takich jak lodówki i pralki.
- Analizy przepływowe w różnego rodzaju kanałach, dyszach i zaworach.
- Analizy z uwzględnieniem reakcji chemicznych.
- Analizy zjawisk w przepływach wielofazowych, takich jak mieszanie, rozpylanie, krzepnięcie, topnienie, wrzenie i kondensacja.
scPOST
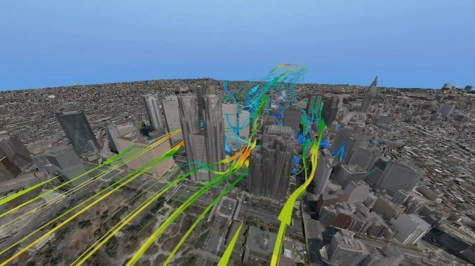
Kliknij aby obejrzeć nagranie wizualizacji z scPOST.
scPOST jest modułem programu Cradle, który służy do analizy i wizualizacji wyników numerycznych symulacji przepływu. Pozwala on na importowanie wyników ze wszystkich pakietów oprogramowania, a następnie przetwarzanie i analizowanie danych. scPOST umożliwia tworzenie różnego rodzaju wizualizacji, takich jak mapy ciśnienia, prędkości, temperatury, iso-powierzchnie, wyznaczenie linii prądu, jak również różnego rodzaju animacje.
Moduł umożliwia tworzenie wykresów i tabel, które pozwalają na analizę danych oraz tworzenie raportów zawierających wyniki analizy, co pozwala na łatwe przekazywanie informacji innym osobom. scPOST posiada także funkcje przetwarzania danych, takie jak filtrowanie, interpolacja czy redukcja wymiarów danych, co pozwala na jeszcze lepszą interpretację wyniku badań.
Funkcjonalności oprogramowania scSTREAM i HeatDesigner
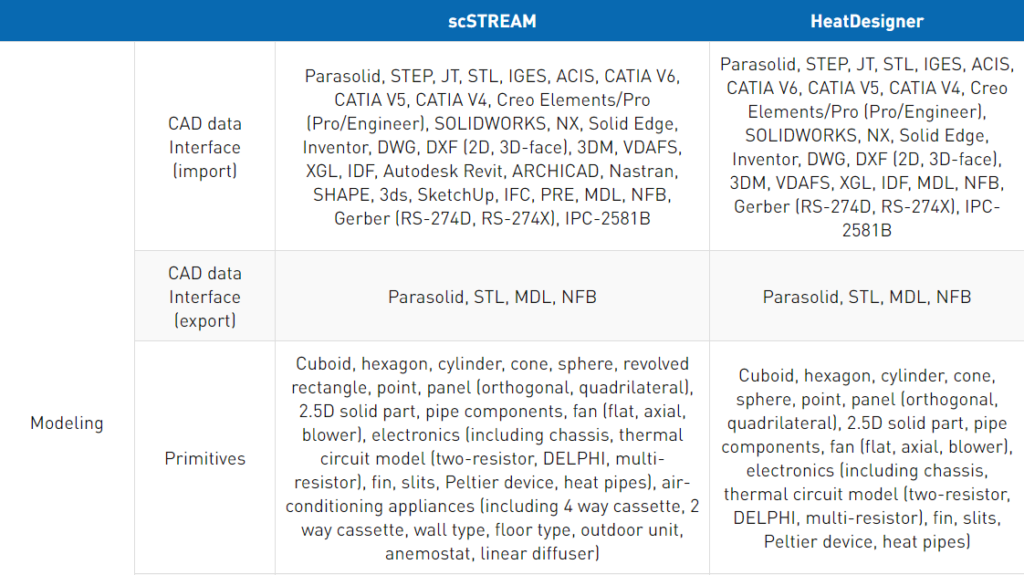
Przejdz tutaj aby zobaczyć pełną listę funkcjonalności
Funkcjonalności oprogramowania scFLOW i SC/Tetra
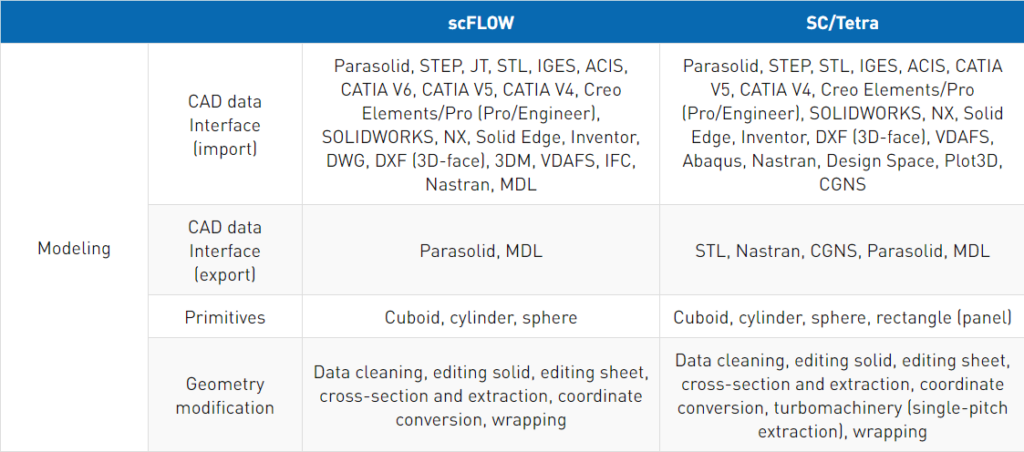
Przejdź tutaj aby zobaczyć pełną listę funkcjonalności

